Topic
Dimensions of Cryptography,
Classical Cryptographic Techniques Block Ciphers (DES, AES) : Feistal Cipher Structure, Simplifies DES, DES, Double and Triple DES, Block Cipher design Principles, AES
Modes of Operations Public-Key Cryptography : Principles Of Public-Key Cryptography, RSA Algorithm, Key Management, Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange, Elgamal Algorithm, Elliptic Curve Cryptography
DES
- Block Cipher Method
- Symmetric Cipher
- Encrypts 64 bit block
Fiestal Cipher - DES takes 16 Rounds
- Data Encryption Standard.
- Converts the plain text to cipher text.
- Block Cipher Algorithm (also Stream Cipher)
- Total of 16 Rounds.
- Text Size = 64 bits
- Key Size = 48 bits ( 8 bits for parity and 8 bits for rearrangement)

**Round Key Generator **
- Permuted Choice 1(PC1) - 8 Parity bits removed, every 8th bit removed. 56 bit
- C0 & D0 - Two equal parts. 28 bit, 28 bit.
- Left Circular Shift (LS) - Move the bits based on round number. For 1 round 1 bit shift, 2 = 2 bit shift.
- C1 & D1 - Added to make key
- LS-LS | C2-C2 are repeated.
- PC2 only
AES
RSA
- Ron R ivest - Adi S hamir - Leonard A dleman, created in 1977.
- The most common & widely used Asymmetric Encryption👁️ algorithm.
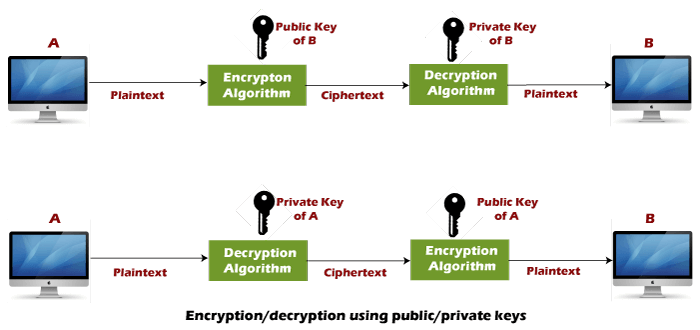
- It creates a pair of commutative keys, i.e., “encrypt with one” “decrypt with the other”.
Generating Keys
- Select two Prime Numbers (P, Q)
P=7 Q=19 - Calculate Product, (P×Q)
N = 133 - Calculate Totient, (P-1) x (Q-1)
T = 108 1 < e < Φ(n)- Select Public Key (E)
E = 29🚀30-1
- Must be a Prime less than Totient.
- Must NOT be a factor of the Totient.
- Select a Private Key (D)
41🚀40+1
- Product of D and E, divided by T must result in a remainder of 1
(D*E) MOD T = 1
Encryption and Decryption
- Encryption
- Decryption
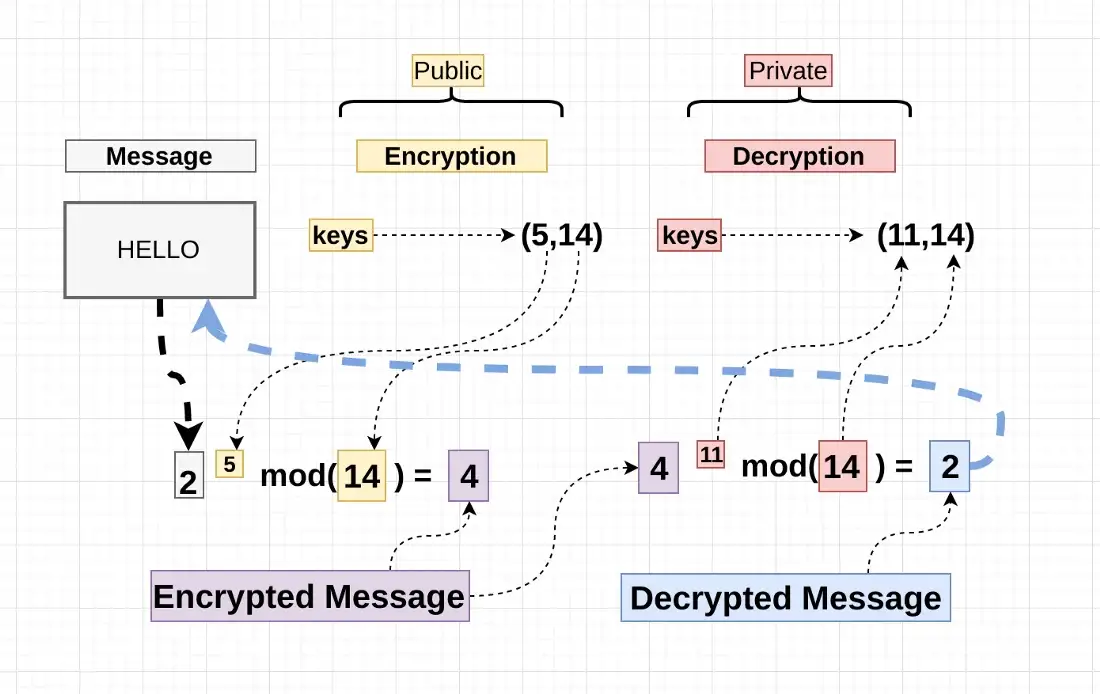
Example Message = 60, Cipher Text = 86 8672
Example(keys switched) Message = 60 Cipher Text = 72
Working
How secure ?
- Security of RSA lies in factoring semi-prime numbers.
- Since the 1991, RSA lab’s 54 prime numbers challenge.
- Biggest Number factored : 829 bits (2020)
- 1024 haven’t been factored for 29 years.
- 1024 bit is standard since 2002
- 2048 bit is standard since 2015
Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange
- Allows two parties to share a shared secret over an unsecured medium.
- Shared Secret is never transmitted, instead values are used to derive secret.

It is same because of discrete log problem.
Elliptic Curve Discrete Log Problem
nA = E, where nA = A dot A dot A
Works similar to exponent & modulo, if you know the point you started at and ended at. It’s hard to guess how many cycle needs to be done to get B

Change it with ECDH
If we have A, B and goes out the field it will wrap around like modulo.

Same security but with smaller key.
Elliptic Curve

ElGamal Algorithm
-
An asymmetric key encryption algorithm based on the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange (DHKE).
-
Created by Taher ElGamal, The “father of SSL” - Secure Sockets layers and A major contributor to Digital Signature Standard (DSS).
-
page aa, page ee
-
Something selected randomly is always 1 < [ ] < p-1
-
Always
g mod prasie random -
Use the rest, and remember the last.


Comments
Post a Comment